Begonia nobmanniae, nom. val., in Edinburgh J. Bot. 68(2): 235. 2011
Primary tabs
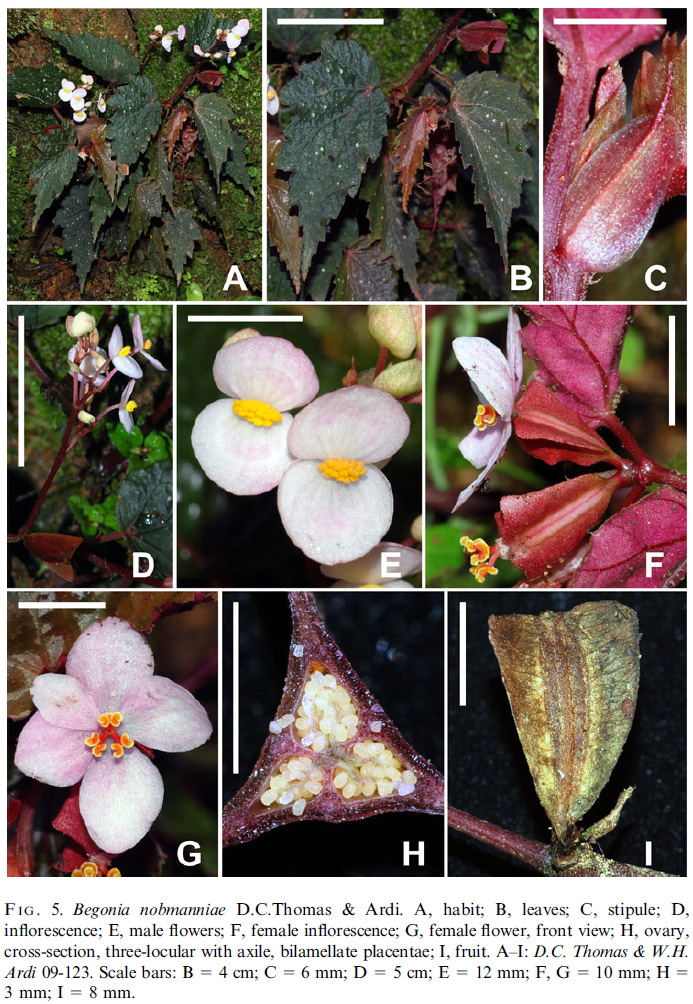
Diagnosis
- Begoniae rachmatii Tebbitt architectura inflorescentiae cum pedunculis inflorescentiae partialis femineae brevibus et ramificatione complici reminiscientia est. A hac specie foliis indivisis et fructibus longioribus (14-17 mm longis nec 8-12 mm) differt. - Type: Indonesia, Sulawesi, Sulawesi Barat, Road Polewali to Mamasa, 03°18'51.9''S, 119°22'24.5''E, 879 m, 7 v 2009, D.C. Thomas & W.H. Ardi 09-123 (holo E; iso BO, L). (Thomas, D.C., Ardi, W.H. & Hughes, M., Nine new species of Begonia (Begoniaceae) from South and West Sulawesi, Indonesia in Edinburgh Journal of Botany 68(2). 2011)
Description
- Perennial, monoecious herb, with erect stems, to c.25 cm tall, glabrous except for a sparse indumentum of microscopic, glandular trichomes, or sometimes exhibiting a sparse indumentum of multicellular, simple trichomes up to c.0.5 mm long on all above-ground vegetative parts. Stems branched; internodes c.2-7 cm long, reddish to brownish.
Leaves alternate; stipules caducous, 8-14 × 4-7 mm, ovate or oblong, with an abaxially prominent midrib that projects shortly at the apex; petioles c.2-4 cm long, greenish or reddish; lamina 5.5-11 × 3-5.5 cm, very asymmetric, ovate, base cordate and lobes not or slightly overlapping, apex acuminate, margin biserrate, teeth not bristle-pointed, adaxial surface dark green and variegated with small white spots, abaxial surface reddish, primary veins 4-5, actinodromous, secondary veins craspedodromous.
Inflorescences: protogynous; female inflorescences 2-flowered or female flowers solitary, basal to male inflorescences, peduncles c.1 mm long; male inflorescences distal to female inflorescences, superinflorescence usually multiple times branched, the axes separating 2-10 partial inflorescences, each consisting of 1-2 monochasia, each monochasium with 1-4 flowers.
Male flowers: pedicels c.8-21 mm long; tepals 2, white or pink, 7-14 × 9-14 mm, broadly ovate to suborbicular, base cordate, apex rounded; androecium of c.30-42 stamens, yellow, filaments up to c.1.5 mm long, slightly fused at the base, anthers up to c.1.1 mm long, obovate, dehiscing through unilaterally positioned slits that are > 1/2 as long as the anther.
Female flowers: pedicels c.1 mm long; tepals 5, pinkish, subequal to unequal, 9-13 × 5-12 mm, elliptic to obovate; ovary ellipsoid, locules 3, placentation axile, placentae bilamellate, wings 3, narrowly triangular, subequal, base rounded to cuneate, apex rounded or truncate, widest at the apex or subapically, style basally shortly fused, 3-branched, each stylodium bifurcate in the stigmatic region, stigmatic surface a spirally twisted papillose band, yellow. Fruiting pedicels up to c.2 mm long.
Fruits ellipsoid, c.14-17 × 3.5-4 mm (excluding the wings), dehiscent, splitting along the wing attachment, wing shape as for ovary, up to 8 mm wide at the widest point; seeds ellipsoidal, c.0.3 mm long, collar cells c.1/2 of the length of the seed. (Thomas, D.C., Ardi, W.H. & Hughes, M., Nine new species of Begonia (Begoniaceae) from South and West Sulawesi, Indonesia in Edinburgh Journal of Botany 68(2). 2011)
Conservation
- Proposed IUCN conservation category: Vulnerable (VU D2). Only a single population has been observed in the field. All available Begonia specimens from A, B, BM, BO, CEB, E, K, L, SING and WAG have been consulted. Hence it must be assumed, at least until more intensive collecting on Sulawesi reveals otherwise, that this species has a very restricted extent of occurrence, which does not fall into any legally protected areas. Moreover, the only known population is adjacent to the Road Polewali-Mamasa, and clearly has been influenced by road construction work. Therefore, it is likely it is "prone to the effects of human activities or stochastic events within a very short time period in an uncertain future" (IUCN, 2001). (Thomas, D.C., Ardi, W.H. & Hughes, M., Nine new species of Begonia (Begoniaceae) from South and West Sulawesi, Indonesia in Edinburgh Journal of Botany 68(2). 2011)
Distribution
Asia-Tropical: Sulawesi (Sulawesi endemic)
Endemic to Indonesia, Sulawesi, West Sulawesi.
See Images for a distribution map, and specimen tab for map of point distribution data of georeferenced specimens.
See Images for a distribution map, and specimen tab for map of point distribution data of georeferenced specimens.
Etymology
- The species is named in honour of the German plant geneticist and Begonia enthusiast Barbara Nobmann, who generously supported an expedition to Sulawesi in 2009.
Notes
- The inflorescence architecture of Begonia nobmanniae, which is characterised by subsessile, sometimes solitary, female flowers and fruits and the complex branching of the male inflorescence, is similar to the conditions found in B. rachmatii. However, Begonia nobmanniae is not just a simple-leaved variant of B. rachmatii, but shows a less delicate growth habit and also differs from it by the larger fruits and tepals, and the more strongly compressed monochasial male partial inflorescences. (Thomas, D.C., Ardi, W.H. & Hughes, M., Nine new species of Begonia (Begoniaceae) from South and West Sulawesi, Indonesia in Edinburgh Journal of Botany 68(2). 2011)
Molecular Systematics
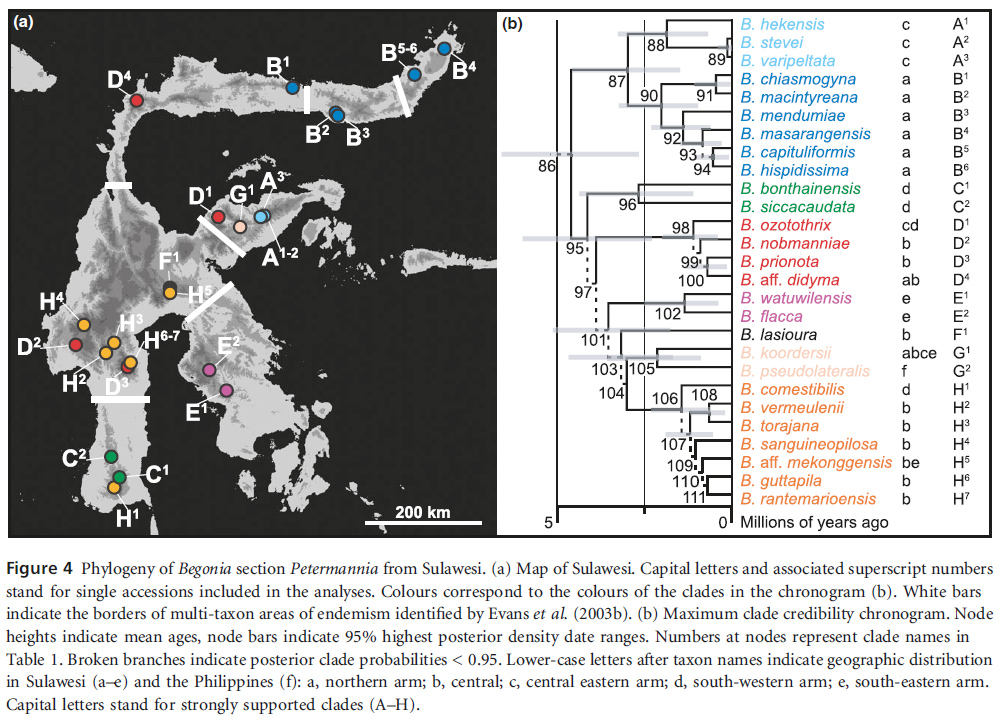
- see Thomas et al., 2012 (Thomas, D.C., Hughes, M., Phutthai, T., Ardi, W.H., Rajbhandary, S., Rubite, R., Twyford, A.D. & Richardson, J.E. 2012: West to east dispersal and subsequent rapid diversification of the mega-diverse genus Begonia (Begoniaceae) in the Malesian archipelago. – Journal of Biogeography 39: 98-113)
- GenBank
 |