Begonia vermeulenii, nom. val., in Edinburgh J. Bot. 68(2): 248. 2011
Primary tabs
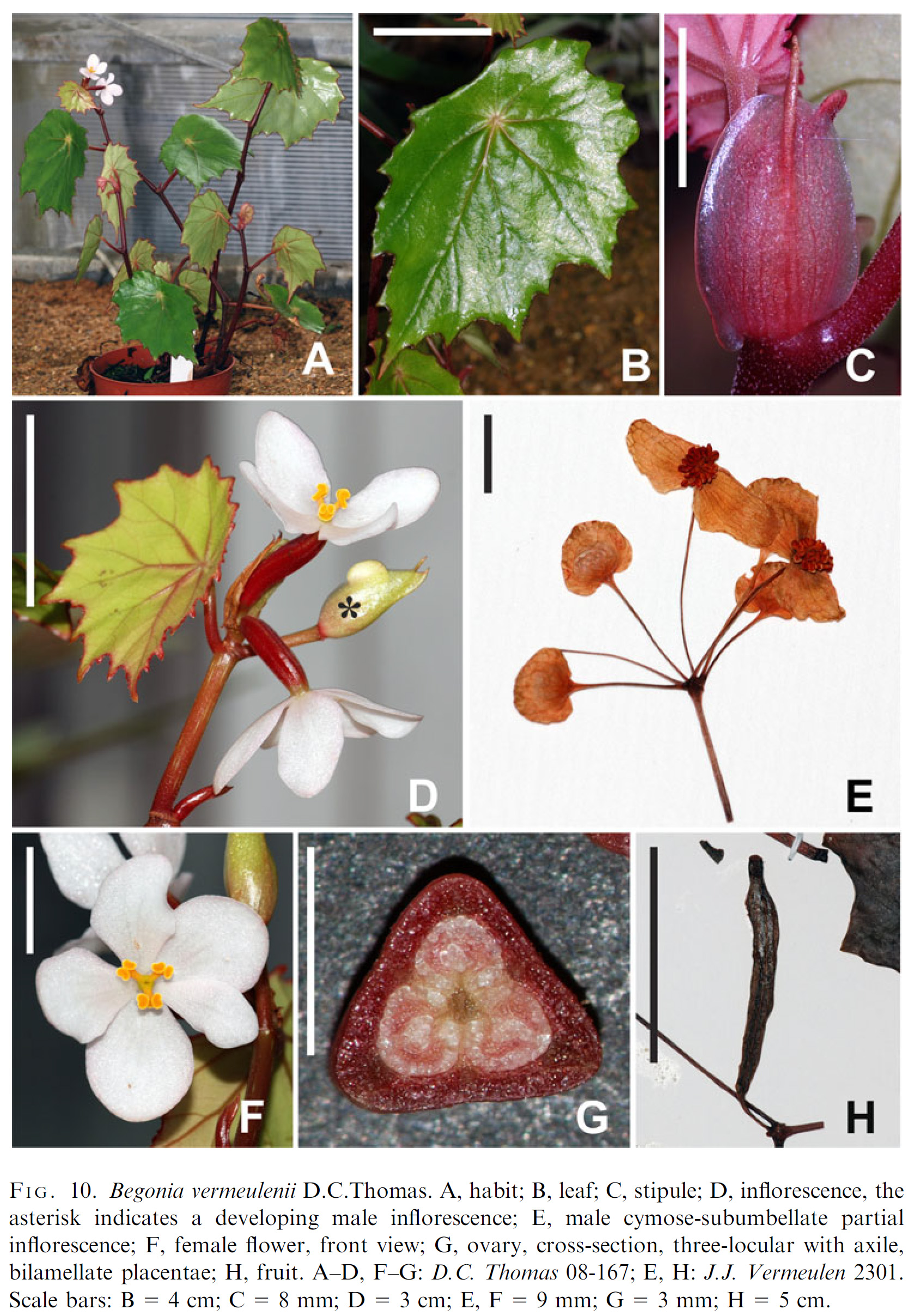
Diagnosis
- Ab aliis speciebus sectionis Petermanniae combinatione characterum foliorum peltatorum et fructibus longis (usque ad 48 mm), fusiformibus, exalatis, carnosis differt. - Type: Indonesia, Sulawesi, Sulawesi Selatan, Buntu area, Kampong, Lokkok, 03°13'S, 119°48'E, 1500-1700 m, 15 ix 2003, J.J. Vermeulen 2301 (holo WAG; iso SING).
Description
- Perennial, monoecious herb, with erect stems, to c.100 cm tall, glabrous except for a sparse indumentum of microscopic, glandular hairs.
Stems branched; internodes c.2-12 cm long, reddish.
Leaves alternate; peltate; stipules caducous, 8-21 × 5-9 mm, ovate to oblong, with an abaxially prominent midrib that projects shortly at the apex; petioles 3.5-9.5 cm long, reddish or greenish; lamina 8-15.5 × 5.5-9.5 cm, very asymmetric, ovate to elliptic, apex acuminate, margin biserrate, irregularly scalloped, teeth not bristle-pointed, adaxial surface dark green and abaxial surface pale green, coriaceous, primary veins 5-6, actinodromous, secondary veins craspedodromous.
Inflorescences: protogynous; female inflorescences 2-flowered, usually positioned one node below the male inflorescences, peduncles c.1 mm long; male inflorescences composed of 1-3 cymose-subumbellate partial inflorescences, each with 2 compressed monochasia with up to 5 flowers, peduncles up to 16 mm long.
Male flowers: pedicels c.10-19 mm long; tepals 2, white, 5-8 × 8-10 mm, broadly ovate to suborbicular, base cordate, apex rounded; androecium of c.35-44 stamens, yellow, filaments up to c.1.4 mm long, slightly fused at the base, anthers c.1.2 mm long, obovate, dehiscing through unilaterally positioned slits that are c.1/2 as long as the anther.
Female flowers: pedicels c.5-10 mm long; tepals 5, white or white tinged with pink, subequal to unequal, 15-17 × 6-11 mm, obovate to elliptic; ovary ellipsoid, wingless, locules 3, placentation axile, placentae bilamellate, style basally shortly fused, 3-branched, each stylodium bifurcate in the stigmatic region, stigmatic surface a spirally twisted papillose band, yellow.
Fruiting pedicels up to c.1 cm long. Fruits fleshy, ellipsoid, c.44-48 × 5-6 mm, indehiscent; seeds ellipsoidal, c.0.3 mm long, collar cells c.1/2-2/3 of the length of the seed.
Habitat
- This is a rainforest floor species, growing on limestone slopes between c.1500 and 1700 m above sea level.
Conservation
- Proposed IUCN conservation category: Vulnerable (VU D2). The known distribution of Begonia vermeulenii falls outside any legally protected area. Furthermore, extensive areas close to the collection site are at best highly degraded or entirely lacking in native vegetation since they have been converted into rice fields and human settlements. Remnant primary forests in the area are often restricted to inaccessible limestone slopes. Although all available Begonia specimens from A, B, BM, BO, CEB, E, K, L, SING and WAG have been consulted, only one collection is known. Other subpopulations could not be detected in an exploration of the area close to the collection site. Hence it must be assumed, at least until more intensive collecting on Sulawesi reveals otherwise, that this species has a very restricted extent of occurrence. Therefore, it is likely that the population "is prone to the effects of human activities or stochastic events within a very short time period in an uncertain future" (IUCN, 2001).
Distribution
Asia-Tropical: Sulawesi (Sulawesi endemic)
Endemic to Indonesia, Sulawesi, South Sulawesi.
See Images for a distribution map, and specimen tab for map of point distribution data of georeferenced specimens.
See Images for a distribution map, and specimen tab for map of point distribution data of georeferenced specimens.
Etymology
- This species is named in honour of the Dutch botanist and orchid specialist Jaap J. Vermeulen.
Notes
- Begonia vermeulenii is one of the most distinct Sulawesi Begonia species because of the conspicuously long, fleshy, wingless fruits and the succulent, peltate leaves. The fleshy fruits, the subumbellate male inflorescences and the succulent leaves indicate a close relationship with other South Sulawesi species including Begonia comestibilis, B. guttapila, B. rantemarioensis, B. sanguineopilosa and B. torajana.
Molecular Systematics
- GenBank
see Thomas et al., 2012 (Thomas, D.C., Hughes, M., Phutthai, T., Ardi, W.H., Rajbhandary, S., Rubite, R., Twyford, A.D. & Richardson, J.E. 2012: West to east dispersal and subsequent rapid diversification of the mega-diverse genus Begonia (Begoniaceae) in the Malesian archipelago. – Journal of Biogeography 39: 98-113)
 |